Mostrando artículos por etiqueta: SolarPaces Symposium
Control System for the High-Flux Solar Furnace of CIE-UNAM in Temixco, Mexico. First Stage
Abstract
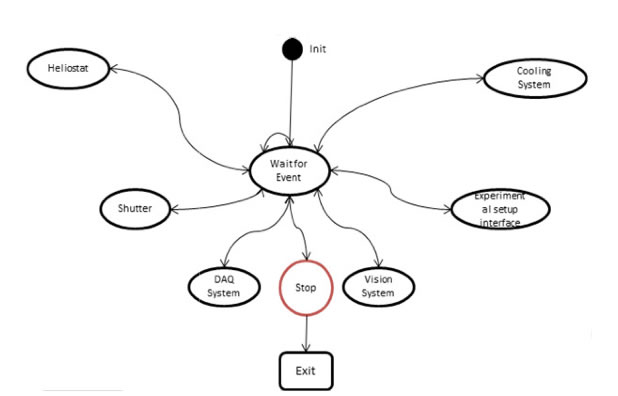
This paper presents the control system design of a new high flux solar furnace that is being developed in Mexico at the Center for Energy Research of the National University of Mexico. The control of the whole system is critical for the correct operation of it. The control system consists of a rugged PC running state machine-based software which manages the operation of all the user interfaces for the furnace systems which are the heliostat, shutter, cooling, visual and data acquisition subsystems, as well as the positioning desk control. The control routines run in real-time controllers dedicated for each subsystem. The computer routines used by the main program and the tests made for characterizing the heliostat follow-up system is also described. Preliminary results obtained shows that the heliostat control presents great versatility due to the type of control it has, including the possibility of accepting feedback through images projected by it.
C.A. Pérez-Rábago, R. Guzmán-Galán, N. Flores-Guzmán, E. Brito, D. Marroqui-García, R. Pérez-Enciso, D. Riveros-Rosas, C.A. Arancibia-Bulnes, C.A. Estrada
Control System for the High-Flux Solar Furnace of CIE-UNAM in Temixco, Mexico. First Stage
Heliostat Testing at a New Facility in Sonora, Mexico
Abstract
A new facility known as Heliostat Test Field has been developed in Mexico. It consists of a solar tower, a laboratory, and 16 heliostats. Three different optical tests have been implemented for the evaluation of heliostats at this installation: sun tracking test, reflected spot test, and deflectometry test. These tests allow the evaluation of tracking, and slope errors of the heliostats. In particular, the later provides detailed slope maps of the reflecting mirrors
Heliostat Testing at a New Facility in Sonora, Mexico
Camilo A. Arancibia-Bulne s, Manuel I. Peña-Cruz, David Marroquín-García, Rafael E. Cabanillas, Carlos A. Pérez-Rábago, David Riveros-Rosas, Jesús F. Hinojosa and Claudio A. Estrada

Heat transfer model of a 1 kWth solar reactor for thermal dissociation of ZnO and SnO2 compressed powders
Abstract
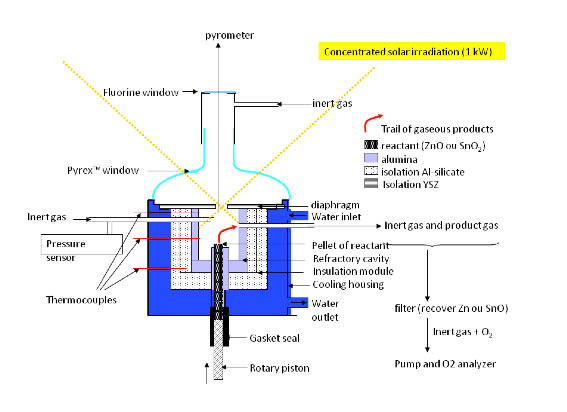
The high-temperature solar processes are one of the promising alternatives to carry out materials transformations for chemical industry, like the calcinations of calcium carbonate for solar production of lime or cement, production of activated charcoal, etc. The production of energy carriers, such as the hydrogen, is a preponderant application that is focused on hydrocarbons substitution, along with very low or null greenhouse gas emissions. This method has the advantage of producing long-term storable and transportable energy carriers from solar energy. The thermochemical hydrogen production through water splitting is one of the most promising routes to obtain “solar hydrogen”.
H.I. Villafán Vidales, S. Abanades, H. Romero-Paredes, C.A. Estrada and C.A. Arancibia-Bulnes
Correction of the Concentrated Sunlight Spot’ s Drift of the CIE-UNAM Solar Furnace
Abstract
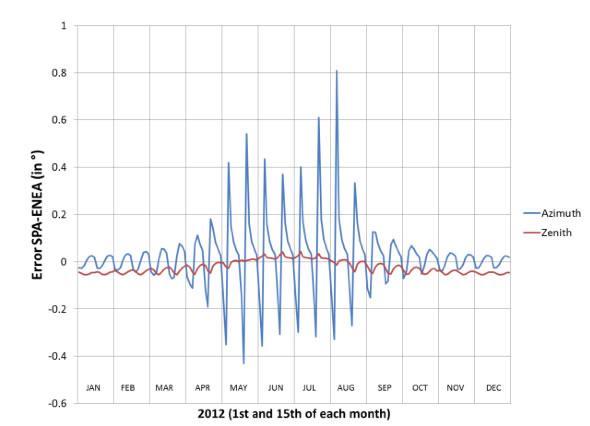
This paper discusses the methods implemented for the solution of the drift and backslash problems in the heliostat of the High Radiative Flux Solar Furnace recently built at the Center for Energy Research of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, located at the geographical coordinates 18° 50' 24" North and 99° 15' 00" West. To solve the observed drift, various algorithms were analyzed for the calculation of the solar vector,and a closed loop through an electronic device was implemented which makes corrections to the position of the heliostat. Drift was corrected by means of unbalancing the heliostat.
R. Pérez-Enciso, E. Brito-Bazan, C. A. Arancibia-Bulnes, D. Riveros-Rosas, C. A. Perez-Rábago, J.J.Quiñones, C. A. Estrada
Correction of the Concentrated Sunlight Spot’ s Drift of the CIE-UNAM Solar Furnace